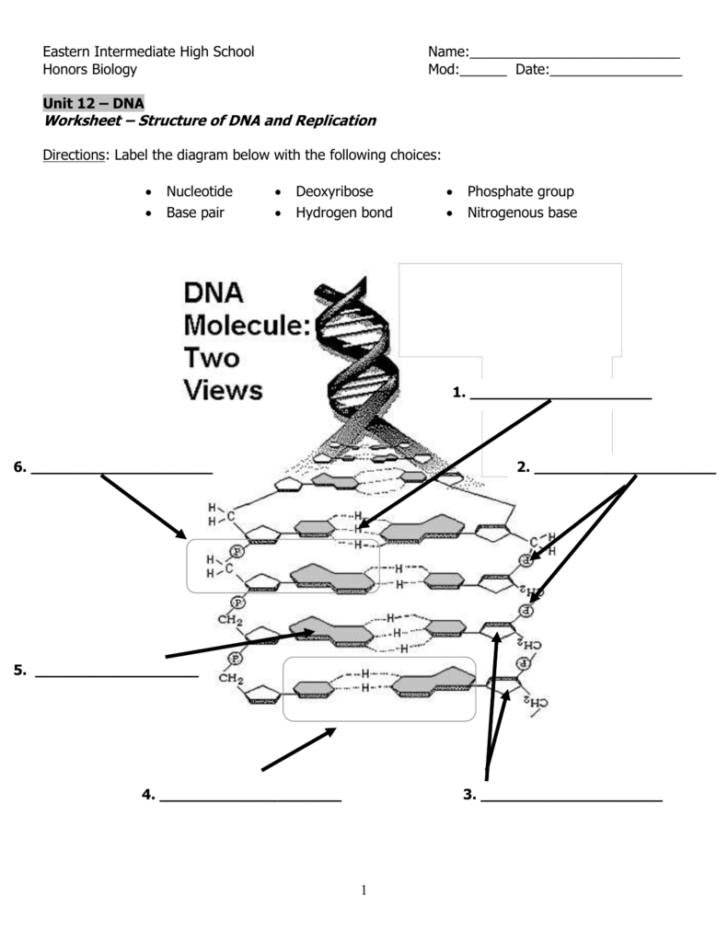
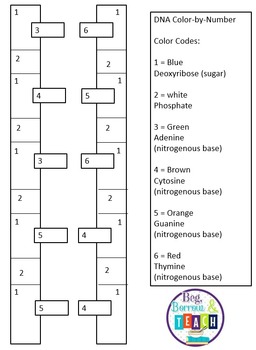
40 dna structure and replication worksheet
› books › NBK9944Heredity, Genes, and DNA - The Cell - NCBI Bookshelf The results of this analysis indicated that all of the heavy DNA had been replaced by newly synthesized DNA with a density intermediate between that of heavy (15 N) and that of light (14 N) DNA molecules. The implication was that during replication, the two parental strands of heavy DNA separated and served as templates for newly synthesized ... › a › dna-structure-and-functionDNA function & structure (with diagram) (article) | Khan Academy DNA structure and function. This is the currently selected item. Next lesson. ... Leading and lagging strands in DNA replication. Transcription and mRNA processing.
› watch(OLD VIDEO) DNA Replication: The Cell's Extreme Team Sport This old video has been updated here: Learn the steps of DNA replication, the enzymes involved, and what it means to be a leadin...

Dna structure and replication worksheet
› about-genomics › fact-sheetsDeoxyribonucleic Acid (DNA) Fact Sheet - Genome.gov Aug 24, 2020 · The importance of DNA became clear in 1953 thanks to the work of James Watson*, Francis Crick, Maurice Wilkins and Rosalind Franklin. By studying X-ray diffraction patterns and building models, the scientists figured out the double helix structure of DNA - a structure that enables it to carry biological information from one generation to the next. basicbiology.net › micro › geneticsTranscription and Translation | Basic Biology Aug 31, 2020 · A strand of DNA contains a chain of connecting nucleotides. Each nucleotide contains a sugar, and a nitrogenous base and a phosphate group. There is a total of four different nitrogenous bases in DNA: adenine (A), thymine (T), guanine (G), and cytosine (C). A strand of DNA is almost always found bonded to another strand of DNA in a double helix. › study-guides › biologyThe Structure of Prokaryote and Eukaryote Cells - CliffsNotes The membrane is therefore referred to as a fluid mosaic structure. Within the fluid mosaic structure, proteins carry out most of the membrane’s functions. The “Movement through the Plasma Membrane” section later in this chapter describes the process by which materials pass between the interior and exterior of a cell.
Dna structure and replication worksheet. sciencenotes.org › dna-vs-rna-similarities-andDNA vs RNA - Similarities and Differences - Science Notes and ... Aug 23, 2020 · Usually, DNA is a double-stranded molecule that forms a double helix, while RNA is a single stranded molecule. Rarely, DNA takes other forms, such as triple-strand DNA and quadraplex DNA. Similarly, double-stranded RNA (dsRNA) occurs in some viruses. DNA uses the bases adenine, thymine, guanine, and cytosine. › study-guides › biologyThe Structure of Prokaryote and Eukaryote Cells - CliffsNotes The membrane is therefore referred to as a fluid mosaic structure. Within the fluid mosaic structure, proteins carry out most of the membrane’s functions. The “Movement through the Plasma Membrane” section later in this chapter describes the process by which materials pass between the interior and exterior of a cell. basicbiology.net › micro › geneticsTranscription and Translation | Basic Biology Aug 31, 2020 · A strand of DNA contains a chain of connecting nucleotides. Each nucleotide contains a sugar, and a nitrogenous base and a phosphate group. There is a total of four different nitrogenous bases in DNA: adenine (A), thymine (T), guanine (G), and cytosine (C). A strand of DNA is almost always found bonded to another strand of DNA in a double helix. › about-genomics › fact-sheetsDeoxyribonucleic Acid (DNA) Fact Sheet - Genome.gov Aug 24, 2020 · The importance of DNA became clear in 1953 thanks to the work of James Watson*, Francis Crick, Maurice Wilkins and Rosalind Franklin. By studying X-ray diffraction patterns and building models, the scientists figured out the double helix structure of DNA - a structure that enables it to carry biological information from one generation to the next.








0 Response to "40 dna structure and replication worksheet"
Post a Comment